Essential De-escalation Techniques for Patient-Centered Care
04 Feb 2025 By: Mary Dellosa
Updated

De-escalation strategies are specialized communication and behavioral techniques used to defuse high-tension situations and prevent patient agitation from turning into aggression. These methods prioritize calm speech, active listening, and non-threatening body language to create a safe environment for both staff and patients. For example, if a patient becomes loud due to a long wait time, a staff member might use a soft tone and offer a small choice, such as waiting in a different area, to help the patient regain a sense of control and calm down.
In my years on the front lines of patient care, I’ve learned that a tense moment can turn a whole day sideways if you don’t have the right tools to handle it. I’ve seen how a simple change in posture or a truly empathetic ear can stop a conflict before it even starts, saving everyone involved from a lot of stress. In this article, I will explain the most effective de-escalation strategies for various medical settings and walk you through how to implement these techniques to keep your clinic safe and compassionate.
Understanding De-escalation in Healthcare
What Is De-escalation?
De-escalation refers to strategies and techniques used to prevent, defuse, or resolve conflicts before they escalate into aggression or violence. In healthcare, it involves using calm communication, active listening, and non-threatening behavior to reduce tension between patients and providers.
Why De-escalation Strategies Matter in Healthcare
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) 75% of workplace assaults happen in healthcare, affecting nurses, doctors, and ER staff. Effective de-escalation strategies can:
✅ Prevent agitation from turning into aggression
✅ Reduce violence and improve staff safety
✅ Build patient trust and satisfaction
✅ Lower stress for patients and staff
✅ Foster a compassionate care environment
Patients in distress may act irrationally, so healthcare professionals need strong de-escalation skills to handle these tough situations effectively.
Core De-escalation Strategies for Healthcare Professionals
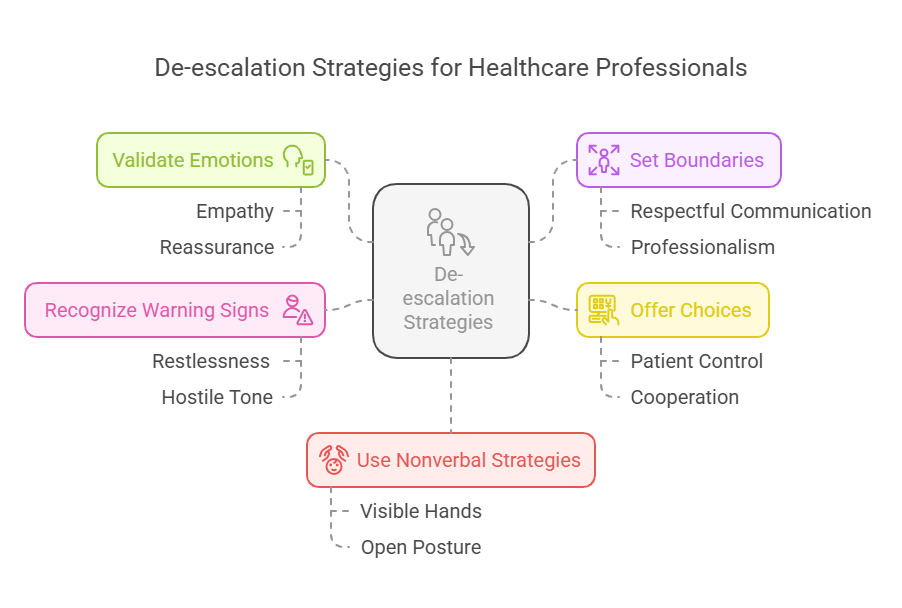
1. Stay Calm and Reassuring
Patients reflect the emotions around them. When healthcare staff stay calm, composed, and empathetic, patients feel heard and understood.
- Speak softly and slowly
- Never raise your voice
- `Keep a relaxed open posture
- Maintain gentle eye contact without staring
A soothing voice and body language can quickly reduce emotional intensity.
2. Use Active Listening
Upset patients need to feel heard.Active listening is a key de-escalation strategy.
- Nod and acknowledge concerns (“I see why you feel that way.”)
- Paraphrase their words (“You’re frustrated about the wait, right?”)
- Avoid interrupting or dismissing emotions
- Ask open-ended questions (“Can you tell me more about that?”)
3. Validate the Patient’s Emotions
Empathy helps prevent escalation, even when the issue can’t be fixed immediately.
What NOT to say:
“Calm down.”
“This isn’t a big deal.”
“There’s nothing I can do.”
What TO say:
“I see why this is frustrating.”
“That must be tough. Let’s find a solution.”
“I appreciate your patience and want to help.”
Validation reassures patients that their feelings matter, even if you don’t agree.
4. Set Clear, Respectful Boundaries
Empathy is key, but clear limits must be set when patients become aggressive.
❌ “Stop yelling, or I won’t help you.”
✅ “I want to assist, but we need a respectful conversation.”
Boundaries ensure respect while keeping professionalism intact.
5. Offer Choices to Give Patients Control
Patients often feel powerless. Small choices help restore control and ease frustration.
❌ “You need to wait.”
✅ “Would you like to wait here or in the lounge?”
❌ “Take this medication now.”
✅ “Would you like to take it now or after you eat?”
Empowering patients reduces stress and improves cooperation.
6. Recognize Early Warning Signs and Act Quickly
De-escalation works best before agitation peaks. Spotting early signs helps prevent escalation.
Warning signs:
– Restlessness or pacing
– Clenched fists or tense posture
– Rapid speech or loud talking
– Hostile tone or aggressive questions
When you notice these, use calm communication, validation, and de-escalation techniques to redirect emotions.
7. Use Nonverbal De-escalation Strategies
Body language plays a key role in calming distressed patients.
Do this:
1. Keep hands visible, avoid crossing arms
2. Use an open, relaxed posture
3. Maintain personal space
4. Smile gently or nod to show understanding
Avoid this:
1. Pointing fingers (feels accusatory)
2. Standing too close (feels intimidating)
3. Making sudden movements (causes anxiety)
A non-threatening posture builds safety and trust.
De-escalation Strategies in Different Healthcare Settings
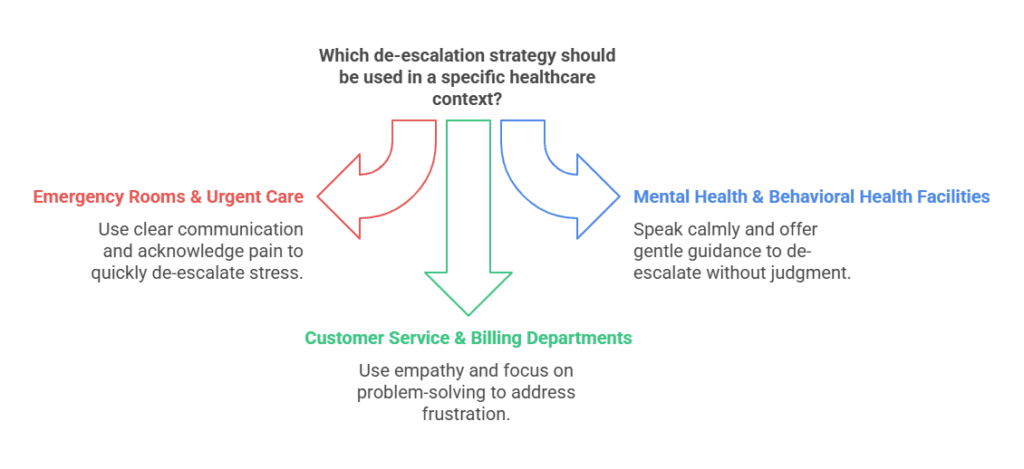
1. Emergency Rooms & Urgent Care
ER patients face stress, pain, and fear. Quick de-escalation is key.
-Use short, clear sentences
-Acknowledge pain and explain next steps
2. Mental Health & Behavioral Health Facilities
Patients may need specialized de-escalation approaches.
-Speak calmly and without judgment
-Avoid pressure; offer gentle guidance
3. Customer Service & Billing Departments
Patients may be frustrated with medical billing or insurance issues.
-Use empathy (“I know this is frustrating. Let’s find a solution.”)
-Avoid arguing; focus on problem-solving
Why De-escalation Strategies Are Essential in Patient-Centered Care
Mastering de-escalation isn’t just about preventing conflict, it builds a safer, more compassionate healthcare environment.
-Patients feel respected and understood
-De escalation training for Healthcare workers face less stress and burnout
-Positive communication improves patient care
By staying calm, listening actively, and using proactive communication, healthcare professionals can turn tough moments into trust-building opportunities.
Incorporating de-escalation strategies extends beyond direct patient care. Frontline communication plays a pivotal role in shaping patient experiences. This is where HelpSquad’s virtual receptionists can add significant value.
How Virtual Receptionists Support De-escalation
HelpSquad’s virtual receptionists expertly manage patient interactions with empathy and efficiency. They help by:
- Managing High Call Volumes – Reducing wait times to ease frustration.
- Providing Clear Communication – Setting accurate expectations about appointments and policies.
- Demonstrating Empathy – Using active listening and compassionate responses to calm concerns early.
By leveraging HelpSquad’s services, healthcare providers can ensure that patient interactions are handled with the utmost care, aligning with de-escalation principles and promoting a patient-centered approach.
FAQ
What is de-escalation in healthcare?
De-escalation is the process of calming a tense or potentially aggressive situation between a patient and healthcare staff. It focuses on communication, empathy, and understanding to prevent conflicts from escalating into crises.
Why is de-escalation important in healthcare settings?
It helps protect both patients and staff from harm, reduces workplace stress, and promotes a safe and supportive environment. Effective de-escalation also improves patient trust and overall satisfaction with care.
What are the key de-escalation techniques every healthcare worker should know?
Core techniques include staying calm, maintaining a neutral tone, giving patients personal space, using active listening, and showing empathy. The goal is to validate the patient’s feelings and guide the conversation toward cooperation.
How can training help staff handle difficult situations?
Training equips healthcare professionals with communication tools and confidence to respond appropriately under pressure. Regular de-escalation training fosters teamwork, consistency, and better patient outcomes.
What role does empathy play in de-escalation?
Empathy helps staff see the situation from the patient’s perspective. By acknowledging their emotions without judgment, healthcare professionals can ease tension, build trust, and resolve issues more effectively.
Conclusion
De-escalation isn’t just a skill, it’s an essential part of compassionate care. With the right training and support, your team can handle tense situations calmly and safely. Talk to us today to learn how HelpSquad can help your healthcare organization strengthen patient communication and deliver better experiences every day.
Strengthen Your Healthcare Team with Expert Support
Effective de-escalation begins with preparation and communication. Partner with HelpSquad to equip your staff with the tools and support they need to manage patient interactions safely and confidently.


