Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare: Benefits and Implementation
13 Aug 2025 By: Vlade Legaspi
Updated

Robotic process automation in healthcare uses software “bots” to handle repetitive, rule-based work like scheduling, eligibility checks, claim submission, prior auth status checks, and data entry across EHR and payer portals. The upside is faster turnaround, fewer errors, better audit trails for compliance, and less admin burden on staff. The risks are messy workflows, poor data quality, security gaps, and change resistance. Start with a stable, high-volume pilot and clear KPIs.
Why RPA Matters for Healthcare?
Healthcare groups face rising patient loads, high costs, strict rules, and the push for better care. Many problems come from slow, manual tasks and scattered data. RPA fixes this by automating healthcare processes and simple tasks without replacing old systems.
RPA uses bots to copy user steps across apps. It needs less money and setup than old automation. This helps hospitals, clinics, and insurers work better, fast.
RPA also boosts data accuracy and safety. Bots move and enter data with fewer mistakes. This cuts risk and helps meet HIPAA and GDPR rules through clear logs.
RPA saves time for doctors and staff. Bots handle tasks like scheduling, billing, and claims. This reduces delays and improves care for patients.
What are the Key Benefits of RPA in Healthcare?
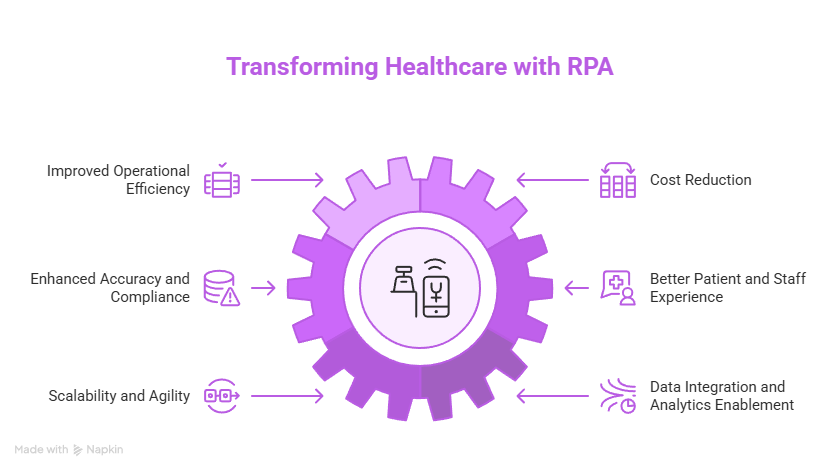
Implementing Robotic Process health care Automation yields a variety of tangible benefits that affect multiple areas of healthcare delivery. These benefits range from operational efficiency to improved compliance and better patient outcomes, delivering both short-term gains and long-term strategic value.
Improved Operational Efficiency
The implementation of Robotic Process Automation in healthcare operations decreases the duration needed to perform repetitive administrative work. The automation of patient registration and prior authorization and billing and claims processing functions reduces processing times from days to minutes. The accelerated processing system enables better patient movement and decreases administrative delays.
Cost Reduction
Automation reduces the labor hours needed to perform routine tasks. While Robotic Process Automation in healthcare is not a substitute for clinical staff, it can offload administrative burdens from highly paid personnel, enabling cost savings and reallocating resources to higher-value activities. Overhead associated with paper handling, manual entry errors, and rework is also reduced.
Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
Manual data entry and repetitive workflows are prone to human error, which can have downstream impacts on billing accuracy, regulatory reporting, and patient safety. Robotic Process Automation in healthcare executes processes consistently and logs every action, improving data accuracy and providing an audit trail crucial for compliance with standards such as HIPAA, ICD coding rules, and payer policies.
Better Patient and Staff Experience
Healthcare patients experience faster registration processes and reduced billing mistakes and expedited service delivery. Healthcare organizations benefit from Robotic Process Automation because it minimizes administrative work and decreases errors. The reduction of administrative monotony leads to improved staff experiences which decreases burnout while boosting job satisfaction. The additional time clinicians spend with patients enables administrative staff to handle exceptions and perform tasks that need both judgment and empathy.
Scalability and Agility
Robotic Process Automation in healthcare bots can be scaled up or down to match demand, such as seasonal spikes in appointments or periodic regulatory reporting. This flexibility allows healthcare organizations to react faster to changing conditions without long procurement cycles or major system overhauls.
Data Integration and Analytics Enablement
The implementation of Robotic Process Automation in healthcare enables the connection of different systems through data extraction and consolidation and transfer operations. Standardized data flows enable more reliable analytics which supports better decision making and population health initiatives and performance measurement.
The healthcare implementation of Robotic Process Automation enables the smooth connection of electronic health records (EHR) with third-party applications and legacy systems through data exchange between platforms. The integration of different healthcare departments and specialists becomes more effective through interoperability which results in better patient care delivery. Real-time monitoring of clinical and operational metrics becomes possible through accurate data flow which enables healthcare leaders to make better decisions about resource allocation and service delivery improvement.
The healthcare industry is witnessing the development of Robotic Process Automation technology which now includes machine learning and natural language processing capabilities. The advanced capabilities of bots enable them to perform predefined rules while adapting to complex workflows and handling unstructured data like physician notes and providing clinical decision support. The advanced automation technology demonstrates potential to transform basic administrative tasks into predictive systems which detect needs before they arise to enhance healthcare results.
Common Healthcare Use Cases for RPA
Robotic Process Automation in healthcare finds applications across the healthcare value chain. Some use cases are back-office focused, while others have direct clinical relevance. The following examples illustrate how RPA can deliver value from registration to revenue cycle management and beyond.
Patient Registration and Scheduling
Bots can automate patient intake by extracting demographic and insurance details from forms, verifying eligibility with payers, and populating electronic health records (EHR) systems. Appointment scheduling bots can manage cancellations, rescheduling, and waitlist notifications, improving utilization and patient satisfaction.
Claims Processing and Revenue Cycle Optimization
Claims submission, validation, denial management, and follow-up are intensive and error-prone. RPA can validate claims for required data elements, cross-check procedural and diagnostic codes, submit claims to payers, and initiate automated appeals or resubmissions for denials, accelerating cash flow and reducing days in accounts receivable.
Prior Authorization
Obtaining prior authorization from payers often involves repetitive retrieval of clinical documents, form filling, and status tracking. RPA can compile necessary clinical notes, attach supporting documentation, submit requests, and monitor responses, significantly decreasing turnaround times for approvals.
Clinical Documentation and Coding Support
Robotic Process Automation in healthcare can assist with clinical documentation improvements by extracting structured information from unstructured notes and alerting coding teams to discrepancies. While RPA does not replace clinical judgment, it can flag missing documentation and prepare coding packages, reducing denials and improving reimbursement accuracy.
Lab and Imaging Result Management
Bots can route lab and imaging results to the correct provider, update patient records, and notify patients or care teams when critical results arrive. This reduces delays in care coordination and helps ensure timely follow-up for abnormal findings.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
The automation of purchase orders and inventory tracking and invoice matching helps to reduce stockouts and overstock situations. RPA can reconcile orders, trigger reorders based on predefined thresholds, and interface with suppliers and financial systems.
Compliance Reporting and Audit Preparation
Robotic Process Automation in healthcare can consolidate data for regulatory reports, populate required forms, and maintain an auditable trail of actions. This reduces manual effort during audits and ensures more accurate and timely reporting to regulatory bodies.
Planning and Preparing for RPA Implementation
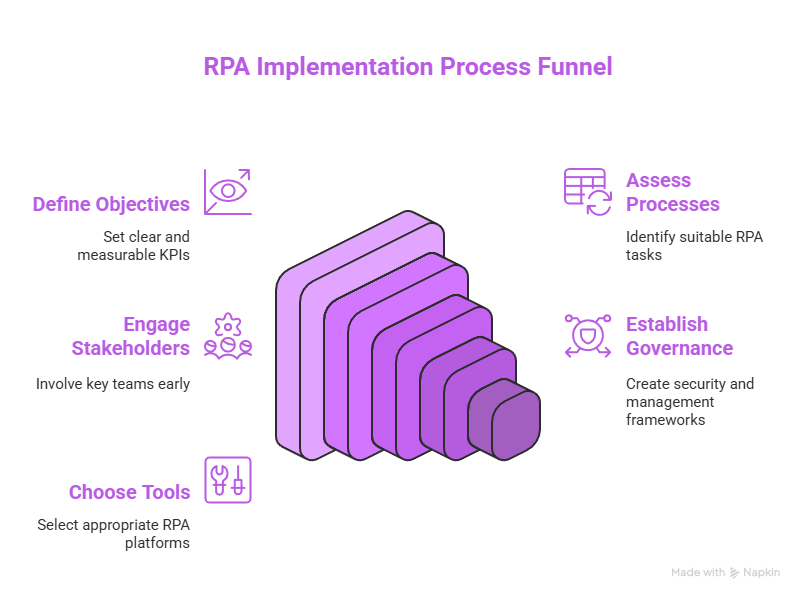
Successful Robotic Process Automation in healthcare implementations require careful planning and alignment with broader organizational goals. RPA should not be pursued as a standalone IT project but as part of a strategy to streamline workflows and improve outcomes.
Define Clear Objectives and KPIs
Begin by identifying business objectives, whether reducing claims denials, improving patient registration times, or shortening prior authorization cycles. Establish measurable KPIs such as time saved per process, error reduction rates, and financial impact to track success.
Process Assessment and Prioritization
Not every task is suitable for Robotic Process Automation in healthcare. Prioritize processes that are rule-based, high-volume, and stable in structure. Process mapping and time-motion studies should be conducted to determine the effort involved and potential ROI. Start with pilot processes that are impactful yet manageable.
Engage Stakeholders Early
The project should start with the involvement of clinical staff together with administrative teams and compliance and IT departments. The process of early engagement enables teams to identify potential issues and discover concealed process differences while obtaining necessary support. The process of explaining healthcare Robotic Process Automation capabilities and limitations to stakeholders helps minimize opposition and establishes practical goals.
How to Establish Governance and Security Frameworks?
Create governance structures to manage robot ownership, change control, exceptions handling, and monitoring. Address privacy and security considerations upfront by ensuring bots adhere to access controls, encryption standards, and audit logging, critical when handling protected health information.
Choose the Right RPA Tools and Partners
Select a Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare platform that integrates with existing systems and supports the necessary security and scalability requirements. Evaluate vendor capabilities in healthcare-specific contexts, and consider partnering with experienced implementation teams who understand clinical workflows and regulatory demands.
Implementation Roadmap
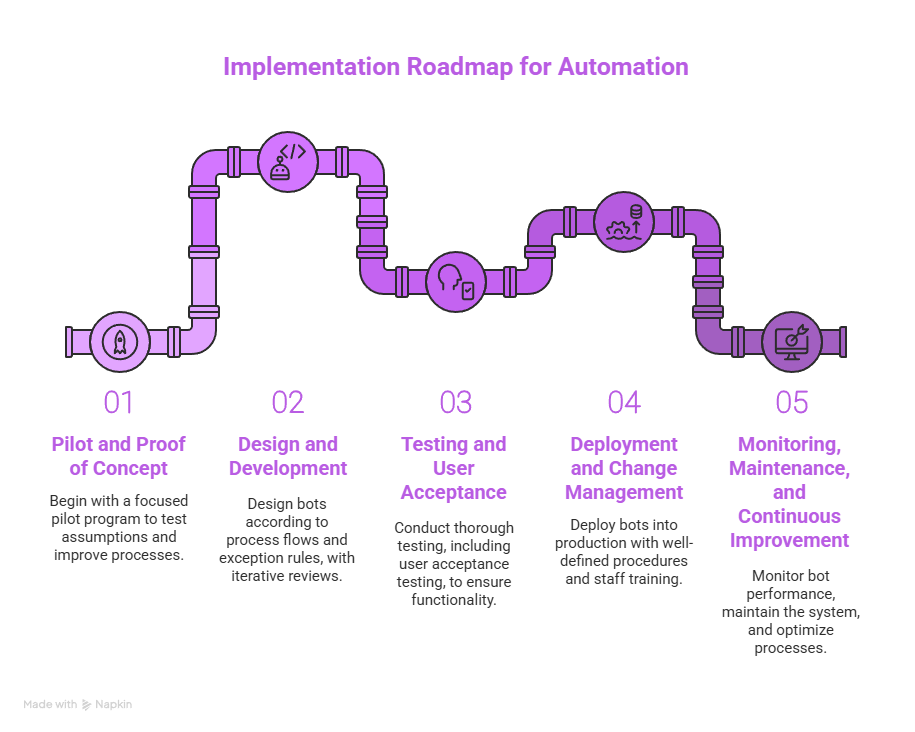
A phased approach reduces risk and accelerates time to value. The following roadmap outlines typical stages from pilot to enterprise rollout.
Pilot and Proof of Concept
Begin with a concentrated pilot program that targets a significant process. The main objective of this phase is to test assumptions while improving process maps and showing quantifiable advantages. The pilot needs to maintain limited scope because this enables quick testing and knowledge acquisition which guides future implementation across the organization.
Design and Development
Design bots according to the documented process flows and exception rules. Include robust error handling and logging. Development should be iterative, with process owners reviewing scripts and test runs to ensure behavior aligns with real-world scenarios. In many cases, organizations leverage principles of app development to create scalable, user-friendly automation tools that integrate smoothly with existing healthcare systems.
Testing and User Acceptance
Testing must include unit tests, integration tests, and user acceptance testing involving the actual users who will interact with bot outputs. Test cases should cover normal flows, edge cases, and security scenarios. Resolve any issues before production deployment.
Deployment and Change Management
The deployment of bots into production requires well-defined operational procedures. The staff who will monitor automated processes and handle exceptions need training and support. The communication of benefits and changes to job responsibilities should be done to maintain morale and clarity.
Monitoring, Maintenance, and Continuous Improvement
The system should include monitoring dashboards to track bot performance and exceptions and SLA adherence. The system should have a maintenance plan for software updates and process changes and scaling requirements. The performance data should be used to optimize the bots and expand the automation to other processes.
Measuring ROI and Impact
Quantifying the impact of Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare is essential to justify continued investment and guide expansion. ROI calculations should include direct and indirect benefits, along with implementation and operating costs.
Direct Financial Benefits
Measure reductions in FTE hours, decreases in claims denial rates, and improvements in billing cycles. Translate time savings into labor cost reductions or redeployment value. For revenue cycle improvements, track increased collections and reduced write-offs as concrete financial gains.
Operational Metrics
Track process cycle times, error rates, and volume handled by bots. Monitor SLA improvements such as faster authorization times or reduced patient wait times. These operational metrics support qualitative benefits like improved patient experience and staff productivity.
Compliance and Risk Reduction
Document the improvements in audit outcomes, the reduction in data entry errors, and the faster regulatory submissions. Quantify risk mitigation wherever possible, such as fines avoided or reduced incident remediation costs due to more accurate record keeping.
What are the Challenges and How to Overcome Them?
The implementation of RPA in healthcare requires active management strategies to overcome the existing challenges despite its clear advantages. Early identification of these issues leads to better chances of achieving sustained success.
Process Variability and Complexity
Healthcare processes exhibit major differences between departments and between clinicians and payers. Standardization stands as a necessary condition for bots to operate effectively in predictable environments. The implementation of process harmonization alongside exception-handling protocols enables organizations to handle variability effectively.
Data Quality and Integration Issues
The quality of data directly affects the success of automation efforts. The automation process requires investment in data cleansing and standardization and validation steps before starting. Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare should first identify data inconsistencies which can lead to improved data governance practices that fix the underlying issues.
Change Resistance and Cultural Barriers
Staff members express concerns about job replacement and doubts about automated system functionality. Organizations should implement open communication about RPA’s function to enhance staff capabilities rather than replace them while offering training programs for role transformation to build trust and drive adoption.
Security and Privacy Concerns
The interaction of bots with PHI requires strict adherence to privacy regulations. The system requires role-based access controls and encryption along with detailed logging capabilities. The compliance team should collaborate with you to make all bot activities auditable while following regulatory standards.
Maintaining and Scaling Automations
RPA operationalization demands continuous maintenance because systems and processes transform over time. A central center of excellence or governance body should be established to oversee bot lifecycle management and performance monitoring while standardizing development practices which enables scalability and resilience.
Best Practices for Sustainable RPA in Healthcare
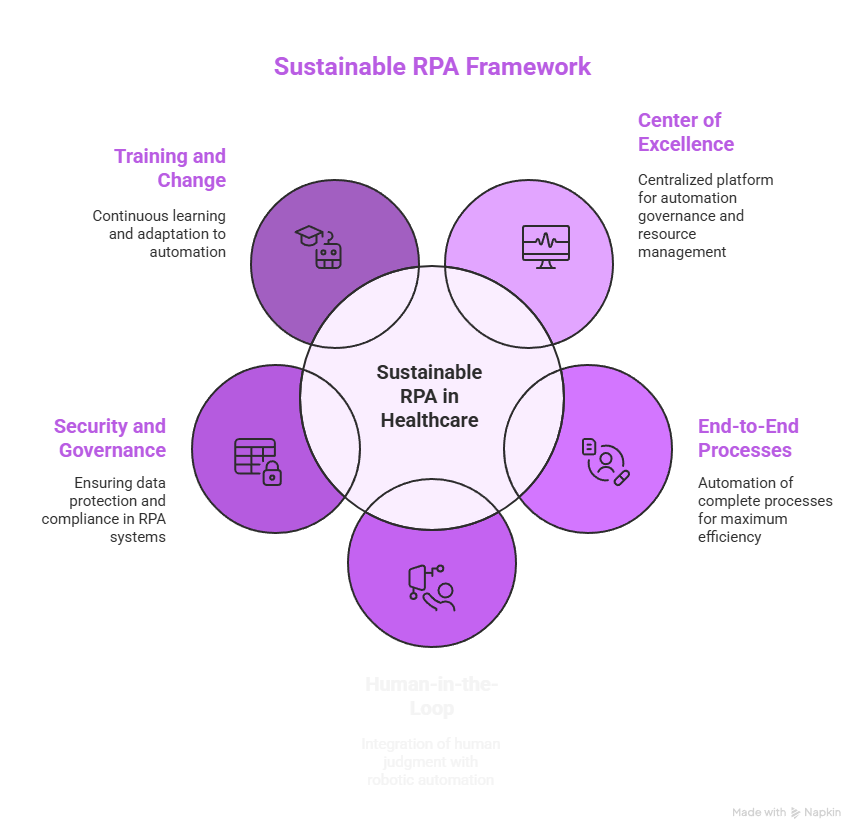
Organizations that follow established best practices achieve better results in RPA initiatives and smooth integration with their operational systems.
Create a Center of Excellence (CoE)
A CoE functions as a centralized platform that unifies automation governance with standardization and shared resource management. The organization manages process selection and development work while enforcing compliance standards through a centralized repository that stores reusable components and institutional knowledge.
Focus on End-to-End Processes
The automation of individual tasks leads to restricted advantages. The target should be end-to-end processes which span from start to finish for patients or transactions. This method delivers the highest possible efficiency improvements while minimizing the number of handoffs that create operational challenges.
Automate Intelligently with Human-in-the-Loop
Some tasks require human judgment. The workflow design should have bots execute repetitive operations and direct exceptional cases to human operators. The combination of robotic speed with human clinical supervision in this hybrid system maintains both quality standards and patient safety.
Prioritize Security and Data Governance
RPA systems need to be integrated into existing IT security and data governance frameworks. The system must implement least-privilege access while storing credentials securely and performing regular security assessments. The incident response plans and disaster recovery tests should include bots as part of their procedures.
Invest in Training and Change Management
The organization should provide continuous training for employees who operate and monitor bots. The organization should develop professional advancement routes which allow employees to move into more important tasks that result from automation. The organization should regularly share automation success stories and collect user feedback to enhance both automation quality and user engagement.
Regulatory Considerations and Ethical Implications
Healthcare automation must navigate regulatory landscapes and ethical responsibilities. Ensuring patient safety, consent, and fairness in automated decision-making is paramount.
Compliance with Health Regulations
Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare deployments must align with HIPAA and other regional health data laws. This includes secure transmission of PHI, strict access controls, and detailed records for auditing purposes. Partnering with legal and compliance teams during design reduces regulatory risk.
Ethical Use of Automation
Automation should enhance, not diminish, patient-centered care. Ethical considerations include transparency about automated communications, ensuring patients can reach human assistance easily, and preventing biased outcomes in any automated triage or decision-support processes.
Clinical Safety and Oversight
When Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare touches clinical workflows, such as result routing or documentation, it must be validated to ensure it does not introduce safety risks. Clinical leaders should participate in approvals and ongoing monitoring to maintain care quality and patient safety.
Future Trends: Intelligent Automation and Beyond
Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare is evolving rapidly, often paired with artificial intelligence (AI) to create intelligent automation capabilities that expand applicability and value in healthcare. These trends signal how automation will deepen its role in care delivery and operations.
Integration with AI and Natural Language Processing
Augmenting Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare with AI enables the automation of unstructured data tasks such as extracting clinical insights from free-text notes, categorizing emails, and interpreting scanned documents. Natural language processing and optical character recognition extend RPA’s reach into previously manual areas.
Hyperautomation and Orchestration
Hyper-automation combines Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare, AI, and process orchestration to automate increasingly complex workflows end-to-end. Orchestration layers manage interactions across bots and human participants, enabling coordinated, adaptive processes that respond to changing clinical contexts.
Patient-Facing Automation
Automation will continue to expand into patient-facing functions such as chatbots for appointment reminders, symptom triage, and virtual assistants that help patients navigate care plans. These tools must prioritize empathy, clarity, and escalation paths to human providers when needed.
Interoperability and Ecosystem Integration
Stronger interoperability standards will make it easier for bots to access and exchange data across EHRs, payer systems, and patient devices. As ecosystems become more connected, automation can support population health, remote monitoring, and value-based care models more effectively.
Trending Now!
The implementation of Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare presents multiple opportunities to decrease expenses while reducing time requirements and enhancing medical care delivery. The article demonstrates six essential RPA applications which include electronic record management and appointment scheduling and billing and claims processing and asset tracking and data analytics and post-treatment care. RPA demonstrates its value through these examples by enhancing precision and decreasing human work while speeding up service delivery. The adoption of RPA has been delayed by high setup expenses and failed trials but the advantages include better patient care and enhanced operational efficiency for providers.
Healthcare systems become more complex so RPA delivers intelligent fast solutions. RPA enables healthcare staff to concentrate on patient care through its capabilities which decrease administrative work and accelerate insurance claims processing and protect data. The UK, US and India have demonstrated increasing success through their real-world implementations. The data and automation capabilities of Telcos enable them to support RPA growth within healthcare. Their participation in this movement enables them to generate new revenue streams while creating meaningful improvements in patient results and system operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Practical Steps to Start
Healthcare organizations should begin their RPA value capture by defining specific goals and selecting appropriate pilot processes while establishing governance structures that maintain safety and compliance standards. The success of RPA depends on measurable outcome tracking and stakeholder involvement from clinical and administrative domains and planned maintenance and expansion strategies.
Healthcare organizations achieve administrative burden reduction and improved accuracy and faster revenue cycles and enhanced patient and staff experiences through proper implementation of Robotic Process Automation. Healthcare organizations that implement these technologies responsibly will achieve better patient-centered care delivery in complex evolving environments through the maturation of intelligent automation and its integration with AI.
Ready to improve care and cut admin work? Join Helpsquad Health and start your free trial today. See how Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare can work for you.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in healthcare?
In the health industry, Robotic Process Automation employs software “bots” to take over the tedious, rule-based actions that the staff frequently perform on computers – such as scheduling, claims processing, data entry, and updating records. These bots are able to carry out pre-defined steps across various existing systems (EHRs, billing platforms, portals) without being a replacement for them, and this consequently leads to faster workflows, less errors, and more time for the staff to actually care for the patients not doing the manual admin job.
What draws attention to the significance of robotic process automation to the healthcare industry right now?
The healthcare industry is going through a lot of issues such as a rise in the number of patients, a increase in the costs, a very strict control and occasionally even under the circumstances where they have to give top care with limited resources. Slow manual processes and the scattered and inaccessible nature of data are the main causes of the problems. Robotic Process Automation in healthcare solution automates routine tasks with speed and consistency, it also enhances data accuracy, helps with HIPAA/GDPR compliance through the provision of clear audit logs, and lastly, it releases clinicians and staff for more valuable tasks.
What issues could be RPA’s lot in the healthcare sector and what remedies will be there?
The most frequent challenges are the inconsistency and complexity of the processes, the substandard quality of the data, the resistance of the personnel, the insecurity of the data, and the long-term maintenance of the automations. In order to cope with these issues, companies will have to standardize workflows, cleanse and validate data, and communicate clearly that RPA supports and does not replace staff, and also conduct strong access controls and audit logging, and have a central Center of Excellence dedicated to managing the bot lifecycle, standards, and scaling.
What makes the insights in this Robotic Process Automation in healthcare article trustworthy?
The article’s insights are based on real healthcare workflows and challenges: manual registration, billing, prior authorization delays, data silos, and compliance pressure. It makes the pain points related to RPA use cases like claims processing, result routing, and audit preparation and outlines the planning steps, governance, and ROI measurement. It also identifies risks like failed pilots, high setup costs, and cultural resistance while giving recommendations like human-in-the-loop design, security-first governance, and ongoing monitoring that are all equally balanced. This mix of practical examples, clear benefits, and honest discussion of challenges adds to the article’s credibility.
What steps should a healthcare organization take to plan and ready the ground for RPA implementation?
What steps should a healthcare organization take to plan and ready the ground for RPA implementation? Automation of processes by robots has been very successful in the healthcare sector when the goals are well laid down and the planning is done well. Thus, the organizations have to: Set clear targets and define performance metrics (like lowering denial rates, reducing registration time, etc.). Identify and classify the processes planned for automation in terms of their amount, the governing rules, and their stability. Engage all relevant parties such as clinical, administrative, IT, and compliance teams right from the start. Establish the governance and security frameworks for access control, audit logging, and change management. Select RPA tools and partners that not only complement the existing systems but also have knowledge of the healthcare laws. Develop a phased roadmap: pilot, design and development, testing, deployment, and ongoing improvement.


