Insourcing vs. Outsourcing: Strategy Guide for Businesses
27 Jul 2023 By: Michael Kansky
Updated
Navigating insourcing and outsourcing is crucial for any business. Our Insourcing vs. Outsourcing Strategy Guide breaks down both approaches. Learn the key differences and how each can be leveraged for maximum efficiency. This guide is your essential tool for enhancing operational effectiveness and driving strategic growth.

Most companies mix insourcing and outsourcing for their needs. Some even blend both for a single function. We’ll explain insourcing and outsourcing, then discuss key decision factors. We’ll guide you in evaluating these factors. Lastly, we’ll share case studies and tips.
Key Takeaways
Insourcing vs. Outsourcing: What’s the Difference?
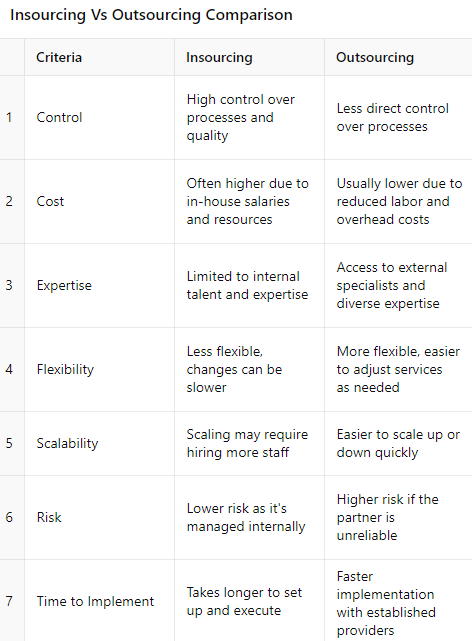
The main difference between insourcing and outsourcing has to do with who’s performing the work:
- Insourcing uses the business’s internal resources to deliver a service or complete a task.
- Business process outsourcing uses the resources of an external organization to deliver a service or complete a task.
Thus, the decision to insource vs. outsource is a strategic business decision.
What Is Insourcing?
Insourcing happens when a business uses its own staff for tasks and services. It requires enough employees with the right skills and experience. When insourcing, businesses must assign people to the task, which may involve training staff, restructuring teams, or hiring new talent.
Benefits of Insourcing
Businesses choose insourcing for a variety of reasons. Key benefits include the following:
1. Control and Flexibility Over Operations
Some businesses prefer to keep control of crucial tasks. Insourcing allows them to manage timelines, methods, security, and teams directly, adapting quickly as needed.
2. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Insourcing strengthens teamwork, communication, and creativity, helping employees collaborate better and boosting team efficiency over time.
3. Better Alignment with Company Culture and Values
Delegating tasks to permanent staff reinforces company culture and values. Employees learn what matters to the company and its preferred ways to work.
Drawbacks of Insourcing
Insourcing has multiple drawbacks. Key drawbacks include the following:
1. Increased Overhead Costs
Insourcing is more expensive due to recruiting, hiring, training, and fixed employee costs. Replacing employees adds to the expense if they leave.
2. Limited Access to Specialized Expertise
Even great recruiters can’t always find or keep every skill needed. Specialized expertise is hard to maintain, and affording all desired in-house skills is often not possible.
3. Potential Capacity Constraints
Building and keeping in-house teams is costly and slow. Rapidly adding staff to meet demands is tough, limiting a business’s ability to scale its own capacity.
What Is Outsourcing?
Outsourcing allows businesses to partner with external companies for services, saving time, reducing costs, improving quality, and handling tasks beyond in-house teams’ capabilities.
Benefits of Outsourcing
Outsourcing offers companies multiple benefits. These benefits include the following:
1. Cost Savings and Increased Efficiency
Outsourcing cuts costs linked to turnover, leave, training, and more. Companies pay set fees for stable services, often making it cheaper and more reliable.
2. Access to Specialized Expertise and Technology
Outsourcing offers immediate access to specialized skills and tech, often beyond what in-house resources can achieve. These aren’t lost to staff changes, providing stability.
3. Scalability and Flexibility in Resource Allocation
Outsourcing allows companies to quickly adjust resources to demand. They can access more resources instantly or reduce them when not needed. This flexibility is crucial.
Drawbacks of Outsourcing
Outsourcing can present multiple drawbacks. These drawbacks include the following:
1. Potential Loss of Control and Visibility
Outsourcing reduces control, as it depends on the external team’s methods, and changes require negotiation.
2. Communication and Cultural Challenges
Outsourcing can cause communication issues, with time zones, schedules, misunderstandings, and cultural differences complicating things.
3. Risk of Dependency on Third-Party Providers
Outsourcing builds knowledge outside the company, risking dependence on third parties. Many companies see this as a risk they’d rather not take.
Factors to Consider When Making a Decision
Choosing between insourcing and outsourcing varies by business. What works for one may not for another. Each task must be assessed individually. Consider these key factors carefully:
1. Nature of the Task or Service
Companies often insource high-stakes tasks for better risk management, compliance, and quality control, especially for confidential or specialized work. Outsourcing is ideal for non-core tasks to reduce costs, speed up work, or access specialized expertise without full-time hires.
2. Cost Considerations
A company’s main cost concern is whether insourcing or outsourcing is cheaper. While outsourcing may save money initially, building in-house expertise can provide long-term value and efficiency, potentially outweighing short-term savings.
3. Resource Availability and Expertise
Outsourcing suits projects needing special skills or resources. If a company has a ready team, insourcing works, but if hiring or training is required, outsourcing may be smarter.
4. Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Companies insource high-risk tasks for more control, while outsourcing low-risk tasks makes sense, as partners can be held accountable.
5. Long-Term Strategic Goals and Objectives
When work is key to a company’s long-term goals, insourcing is safer to protect competitive advantage. For routine, operational tasks, outsourcing is often the logical pick.
Case Studies and Examples
The above sections offer general advice on insourcing vs. outsourcing. Now, let’s explore real-life case studies of companies choosing one over the other.
Successful Insourcing Instances
- Law Firms: The legal industry heavily relies on insourcing due to the high stakes and sensitive information involved. 44% of law firms use in-house teams for most litigation services, and 20% plan to reduce third-party use next year.
- IT Services: Companies have increased IT outsourcing, but many later insource. According to Deloitte, 34% insource after ending outsourcing contracts, and 48% have terminated IT outsourcing early. Insourcing is preferred for greater control.
Successful Outsourcing Instances
- Cybersecurity: Businesses have traditionally hesitated to outsource cybersecurity, but that’s changing. With high demand for top talent, 81% of companies now use third-party vendors for cybersecurity.
- Financial Advisors: The financial advisory industry increasingly outsources to meet client needs, regulations, and digital changes. 99% of advisors using consultants report business improvements.
Hybrid Insourcing-Outsourcing Model
A hybrid model blends insourcing and outsourcing, letting companies hire directly through contracts, not through third-party providers. This approach combines both strategies’ benefits.
Benefits and Considerations of a Hybrid Model
The hybrid model lets companies hire global talent and save money while keeping hires connected to the team. However, language and time zone challenges require investment in onboarding and training for remote success.
Making the Decision: Insourcing or Outsourcing?
When deciding to insource or outsource, businesses should consider costs, risks, control, expertise needs, and long-term goals.
Evaluating the Specific Needs and Goals of the Organization
Businesses should match every task with their needs and goals. Assessing the importance of work to company objectives guides the choice between insourcing and outsourcing.
Assessing the Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Option
Choosing between insourcing and outsourcing requires more than intuition. Companies must weigh each option’s pros and cons, considering costs, risks, control, expertise, and strategic fit.
- How readily can the work be delegated?
- How much scalability and flexibility does the business need?
- What kind of quality control does the business want?
- What kind of oversight and visibility does the business need?
- What are the cost implications?
- How important is it for the business to build institutional knowledge?
- What degree of security risk is the business willing to take on?
Insourcing vs. Outsourcing – What is Right for Your Business
When it comes to insourcing vs. outsourcing, there’s no right or wrong answer. It’s a strategic choice. Insourcing relies on internal resources; outsourcing, on external ones. The best decision aligns with long-term goals and thoroughly weighs pros and cons.
Companies don’t have to decide on insourcing vs. outsourcing alone. Live Help Now experts can guide through all key aspects, helping businesses align work with their needs and weigh insourcing vs. outsourcing benefits and drawbacks.
Trending Now
Over 30 years, global talent sourcing shifted from cost-cutting to finding skilled professionals that enhance business capabilities. Companies like GE outsourced to Mexico for savings, later turning to India and Eastern Europe for specialized skills. Now, businesses hire top talent worldwide to build expert teams in countries like Vietnam and Chile, driving innovation and supporting diverse needs. The choice between insourcing or outsourcing impacts cost, control, and competitiveness.
Insourcing strategy FAQ
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between insourcing and outsourcing requires careful consideration of tasks, costs, resources, risks, and goals. Insourcing offers control but can be costly and lacks specialized skills, while outsourcing saves money and brings expertise but reduces control. Industries like law and IT often insource, while finance and cybersecurity outsource. A hybrid model may suit some companies, depending on their unique needs.
Ready to sidestep these outsourcing blunders and elevate your business operations? Look no further than HelpSquad BPO. With our skilled, bilingual agents ready to handle your customer support, back-office tasks, and research needs starting at just $8.50 per hour, you can boost your efficiency without breaking the bank. Don’t let common mistakes hold you back. Start your trial with HelpSquad today and experience the difference that professional virtual assistants and a 24/7 customer service team can make for your business.


